A game where you have to find the exit of a maze while avoiding enemies. Made with custom 2D CPU raytracing.
Project Overview
I had 6 weeks to make a small 2D ray tracing renderer and 2 weeks to make a small game to demonstrate it. This project taught me a lot about SIMD, optimization structures, and vector math. I implemented point lights, spot lights, mirrors, and rasterization.
The game
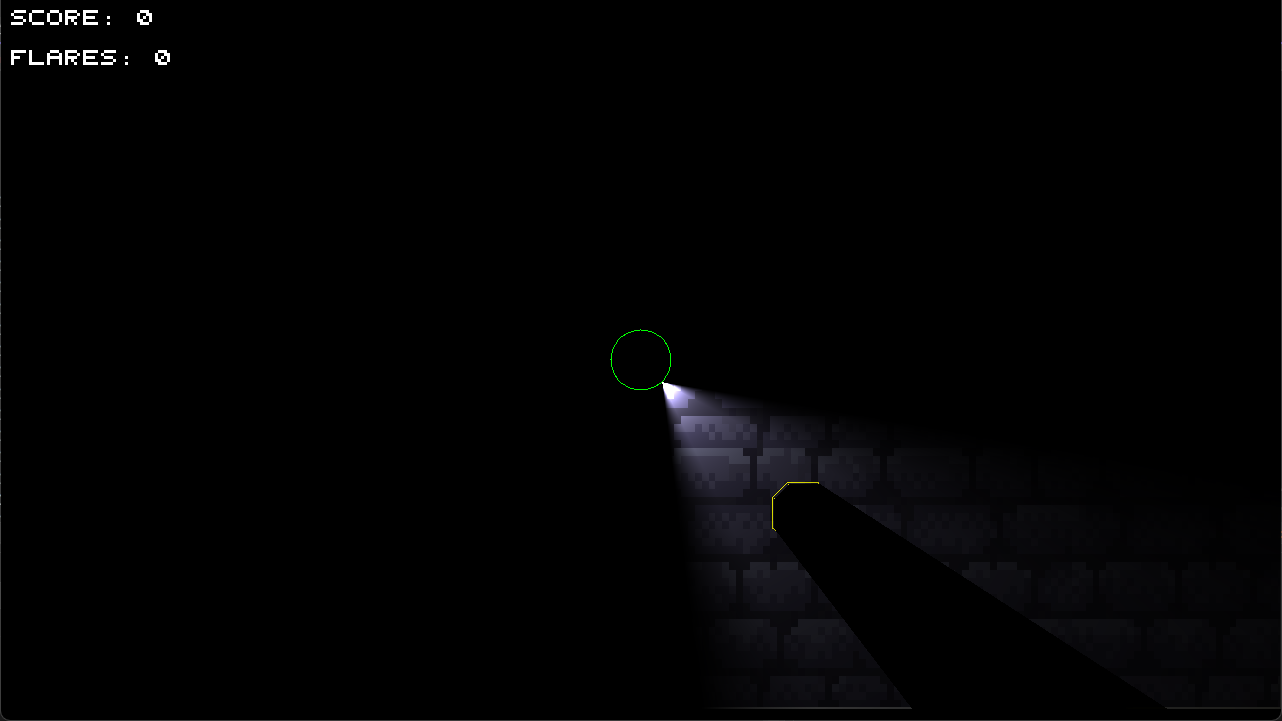
I had two weeks to make a small game that demonstrates my ray tracer. I came up with the idea for the game, the objectives, and the level design. I used Dark Echo for inspiration, but instead of sound, I used light.
The player has to escape a dark maze full of hostile creatures that are attracted to light. He can use his flashlight and throw flares to distract them. Throughout the maze there are treasures that give the player points and more flares.
.jpg)
Gameplay example:
Lights
I started by implementing point lights and spot lights. The spot lights can have soft edges.
I'm calculating the squared distance from the light sources to see if the pixel is in range. In this way I'm avoiding square roots which improves performance.
I'm using dot product to calculate the cone of the spot light. For soft edges, I have 2 cones - inner (normal calculation) and outer (using linear interpolation to blend).
Mirrors
Having a mirror essentially doubles the amount of lights in the level. If the light ray hits a mirror, I calculate the hit position on the mirror and the mirrored position of the light source around the mirror (small white circle in the video below) and calculate as if the light was coming from there.
Occluders
My ray tracer supports lines, circles, and more complex objects:
Optimization
For optimization I used multithreading with OpenMP, SIMD, and I implemented 3 optimization grids. Also, I used the DDA algorithm to improve performance when searching for occluders.
I implemented 3 optimization grids: lights grid, shadows grid, and occluders grid:
- The lights grid culls lights that are too far.
- The shadows grid is used to speed up shadows. If all four corners of a cell are unlit, then we can assume that the pixels inside that cell will be unlit too.
- The occluders grid is used so that we check for intersections only against relevant occluders.